JUC
java
CompletableFuture
1. CompletableFuture和CompletionStage介绍
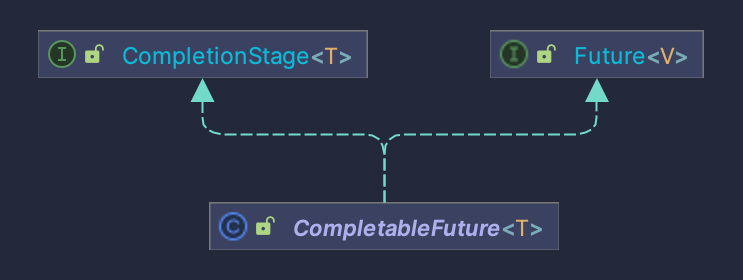
接口CompletionStage
代表异步计算过程中的某一个阶段,一个阶段完成以后可能会触发另外一个阶段。
一个阶段的执行可能是被单个阶段的完成触发,也可能是由多个阶段一起触发
类CompletableFuture
提供了非常强大的Future的扩展功能,可以帮助我们简化异步编程的复杂性,并且提供了函数式编程的能力,可以通过回调的方式处理计算结果,也提供了转换和组合CompletableFuture的方法
它可能代表一个明确完成的Future,也可能代表一个完成阶段(CompletionStage),它支持在计算完成以后触发一些函数或执行某些动作
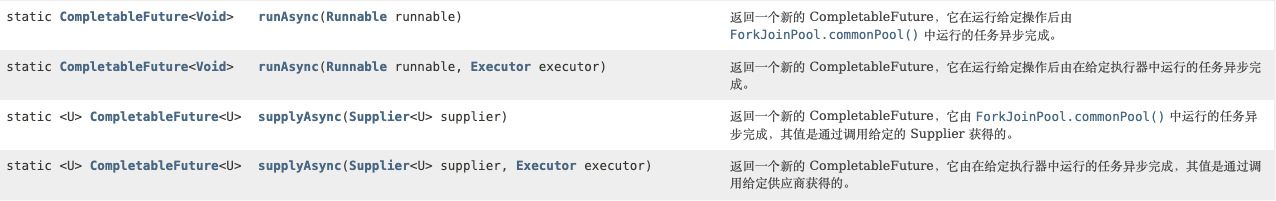
2. 核心的四个静态方法,创建一个异步任务
对于上述Executor参数说明:若没有指定,则使用默认的ForkJoinPoolcommonPool() 作为它的线程池执行异步代码,如果指定线程池,则使用我们自定义的或者特别指定的线程池执行异步代码
Java @Slf4j ( topic = "c.FutureTest1" )
public class FutureTest1 {
public static void main ( String [] args ) throws ExecutionException , InterruptedException {
test1 ();
test2 ();
}
private static void test2 () throws ExecutionException , InterruptedException {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors . newFixedThreadPool ( 3 );
CompletableFuture < Void > future1 = CompletableFuture . runAsync (() -> {
log . debug ( "111" );
try {
TimeUnit . SECONDS . sleep ( 1 );
} catch ( InterruptedException e ) {
throw new RuntimeException ( e );
}
}, executorService );
log . debug ( "{}" , future1 . get ());
CompletableFuture < String > future2 = CompletableFuture . supplyAsync (() -> {
log . debug ( "222" );
try {
TimeUnit . SECONDS . sleep ( 1 );
} catch ( InterruptedException e ) {
throw new RuntimeException ( e );
}
return "hello supplyAsync" ;
}, executorService );
log . debug ( "{}" , future2 . get ());
executorService . shutdown ();
}
private static void test1 () throws InterruptedException , ExecutionException {
CompletableFuture < Void > future1 = CompletableFuture . runAsync (() -> {
log . debug ( "111" );
try {
TimeUnit . SECONDS . sleep ( 1 );
} catch ( InterruptedException e ) {
throw new RuntimeException ( e );
}
});
log . debug ( "{}" , future1 . get ());
CompletableFuture < String > future2 = CompletableFuture . supplyAsync (() -> {
log . debug ( "222" );
try {
TimeUnit . SECONDS . sleep ( 1 );
} catch ( InterruptedException e ) {
throw new RuntimeException ( e );
}
return "hello supplyAsync" ;
});
log . debug ( "{}" , future2 . get ());
}
}
运行结果:
Bash # test1
11 :52:54.186 c.FutureTest1 [ ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-1] - 111
11 :52:55.192 c.FutureTest1 [ main] - null
11 :52:55.200 c.FutureTest1 [ ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-1] - 222
11 :52:56.204 c.FutureTest1 [ main] - hello supplyAsync
# test2
11 :52:56.208 c.FutureTest1 [ pool-1-thread-1] - 111
11 :52:57.210 c.FutureTest1 [ main] - null
11 :52:57.212 c.FutureTest1 [ pool-1-thread-2] - 222
11 :52:58.217 c.FutureTest1 [ main] - hello supplyAsync
CompletableFuture减少阻塞和轮询,可以传入回调对象,当异步任务完成或者发生异常时,自动调用回调对象的回调方法。
示例代码:
Java @Slf4j ( topic = "c.FutureTest2" )
public class FutureTest2 {
public static void main ( String [] args ) {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors . newFixedThreadPool ( 3 );
CompletableFuture < Integer > future = CompletableFuture . supplyAsync (() -> {
log . debug ( "------come in" );
int result = ThreadLocalRandom . current (). nextInt ( 10 );
try {
TimeUnit . SECONDS . sleep ( 1 );
} catch ( InterruptedException e ) {
throw new RuntimeException ( e );
}
if ( result > 5 ) {
int i = 1 / 0 ;
}
log . debug ( "------ result: {}" , result );
return result ;
}, executorService ). whenComplete (( v , e ) -> {
if ( e == null ) {
log . debug ( "计算完成,结果是: {}" , v );
}
}). exceptionally ( e -> {
e . printStackTrace ();
log . error ( "异常报错" , e );
return null ;
});
log . debug ( "主线程执行其他任务" );
executorService . shutdown ();
}
}
正常执行:
Bash 11 :58:22.495 c.FutureTest2 [ pool-1-thread-1] - ------come in
11 :58:22.495 c.FutureTest2 [ main] - 主线程执行其他任务
11 :58:23.501 c.FutureTest2 [ pool-1-thread-1] - ------ result: 5
11 :58:23.506 c.FutureTest2 [ pool-1-thread-1] - 计算完成,结果是: 5
报错:
CompletableFuture优点:
异步任务结束 时,会自动回调某个对象的方法
主线程设置好回调后,不用关心异步任务的执行,异步任务之间可以顺序执行
异步任务出错 时,会自动回调某个对象的方法
3. 案例-电商网站的比价需求
3.1 需求分析
电商网站比价需求分析:
需求说明:
同一款产品,同时搜索出同款产品在各大电商平台的售价
同一款产品,同时搜索出本产品在同一个电商平台下,各个入驻卖家售价是多少
输出返回:
出来结果希望是同款产品的在不同地方的价格清单列表,返回一个List<String>《Mysql》 in jd price is 88.05 《Mysql》 in taobao price is 90.43
解决方案,对比同一个产品在各个平台上的价格,要求获得一个清单列表
step by step,按部就班,查完淘宝查京东,查完京东查天猫....
all in,万箭齐发,一口气多线程异步任务同时查询
3.2 代码
Java @Slf4j ( topic = "c.FutureTest3" )
public class FutureTest3 {
public static void main ( String [] args ) {
List < NetMall > list = Arrays . asList ( new NetMall ( "jd" ),
new NetMall ( "taobao" ),
new NetMall ( "dangdang" ));
long startTime = System . currentTimeMillis ();
List < String > l1 = getPrice ( list , "mysql" );
for ( String e : l1 ) {
log . debug ( "{}" , e );
}
long endTime = System . currentTimeMillis ();
log . debug ( "costTime: {} ms" , endTime - startTime );
log . debug ( "=====================================" );
long startTime2 = System . currentTimeMillis ();
List < String > l2 = getPriceByCompletableFuture ( list , "mysql" );
for ( String e : l2 ) {
log . debug ( "{}" , e );
}
long endTime2 = System . currentTimeMillis ();
log . debug ( "costTime: {} ms" , endTime2 - startTime2 );
}
private static List < String > getPrice ( List < NetMall > list , String productName ) {
return list . stream ()
. map ( mall ->
String . format ( "《%s》 in %s price is %.2f" ,
productName ,
mall . getNetMallName (),
mall . calcPrice ( productName )))
. collect ( Collectors . toList ());
}
private static List < String > getPriceByCompletableFuture ( List < NetMall > list , String productName ) {
return list . stream ()
. map ( mall ->
CompletableFuture . supplyAsync (() ->
String . format ( "《%s》 in %s price is %.2f" ,
productName ,
mall . getNetMallName (),
mall . calcPrice ( productName ))))
. collect ( Collectors . toList ())
. stream ()
. map ( CompletableFuture :: join )
. collect ( Collectors . toList ());
}
}
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
class NetMall {
private String netMallName ;
public double calcPrice ( String productName ) {
try {
TimeUnit . SECONDS . sleep ( 1 );
} catch ( InterruptedException e ) {
throw new RuntimeException ( e );
}
return ThreadLocalRandom . current (). nextDouble () * 2 + productName . charAt ( 0 );
}
}
结果:
Bash 12 :22:43.563 c.FutureTest3 [ main] - 《mysql》 in jd price is 109 .78
12 :22:43.572 c.FutureTest3 [ main] - 《mysql》 in taobao price is 110 .58
12 :22:43.572 c.FutureTest3 [ main] - 《mysql》 in dangdang price is 110 .68
12 :22:43.572 c.FutureTest3 [ main] - costTime: 3062 ms
12 :22:43.573 c.FutureTest3 [ main] - =====================================
12 :22:44.584 c.FutureTest3 [ main] - 《mysql》 in jd price is 109 .47
12 :22:44.584 c.FutureTest3 [ main] - 《mysql》 in taobao price is 110 .51
12 :22:44.584 c.FutureTest3 [ main] - 《mysql》 in dangdang price is 110 .38
12 :22:44.584 c.FutureTest3 [ main] - costTime: 1011 ms
4. CompletableFuture常用方法
4.1 获得结果和触发计算
获取结果
public T get()public T get(long timeout,TimeUnit unit)public T join()--->和get一样的作用,只是不需要抛出异常public T getNow(T valuelfAbsent) --->计算完成就返回正常值,否则返回备胎值(传入的参数),立即获取结果不阻塞
主动触发计算
public boolean complete(T value) ---->是否打断get方法立即返回括号值
4.2 对计算结果进行处理
thenApply --->计算结果存在依赖关系,这两个线程串行化 ---->由于存在依赖关系(当前步错,不走下一步),当前步骤有异常的话就叫停handle --->计算结果存在依赖关系,这两个线程串行化 ---->有异常也可以往下走一步
Java @Slf4j ( topic = "c.CompletableFutureApiDemo" )
public class CompletableFutureApiDemo {
public static void main ( String [] args ) throws ExecutionException , InterruptedException , TimeoutException {
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors . newFixedThreadPool ( 3 );
CompletableFuture < Integer > completableFuture = CompletableFuture . supplyAsync (() -> {
try {
TimeUnit . SECONDS . sleep ( 1 );
} catch ( InterruptedException e ) {
e . printStackTrace ();
}
return 1 ;
}, threadPool ). thenApply ( f -> {
log . debug ( "222" );
return f + 2 ;
}). handle (( f , e ) -> {
log . debug ( "333" );
int i = 10 / 0 ;
return f + 2 ;
}). whenComplete (( v , e ) -> {
if ( e == null ) {
log . debug ( "计算结果: {}" , v );
}
}). exceptionally ( e -> {
e . printStackTrace ();
System . out . println ( e . getCause ());
return null ;
});
log . debug ( "主线程执行其他任务" );
threadPool . shutdown ();
}
}
4.3 对计算结果进行消费
接受任务的处理结果,并消费处理,无返回结果
thenAccept
Java @Slf4j ( topic = "c.CompletableFutureApi2Demo" )
public class CompletableFutureApi2Demo {
public static void main ( String [] args ) {
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors . newFixedThreadPool ( 3 );
CompletableFuture . supplyAsync (() -> 1 , threadPool )
. thenApply ( f -> f + 2 )
. thenApply ( f -> f + 2 )
. thenAccept ( r -> log . debug ( "result: {}" , r )); // 5
threadPool . shutdown ();
}
}
对比补充
thenRun(Runnable runnable) :任务A执行完执行B,并且不需要A的结果thenAccept(Consumer action): 任务A执行完执行B,B需要A的结果,但是任务B没有返回值thenApply(Function fn): 任务A执行完执行B,B需要A的结果,同时任务B有返回值
Java @Slf4j ( topic = "c.CompletableFutureApi2Demo" )
public class CompletableFutureApi2Demo {
public static void main ( String [] args ) {
log . debug ( "{}" ,
CompletableFuture . supplyAsync (() -> "result" )
. thenRun (() -> {})
. join ()); //null
log . debug ( "{}" ,
CompletableFuture . supplyAsync (() -> "result" )
. thenAccept ( r -> log . debug ( "{}" , r ))
. join ()); //result null
log . debug ( "{}" , CompletableFuture . supplyAsync (() -> "result" )
. thenApply ( f -> f + 2 )
. join ()); // result2
}
}
CompletableFuture和线程池说明
如果没有传入自定义线程池,都用默认线程池ForkJoinPool
传入一个线程池,如果你执行第一个任务时,传入了一个自定义线程池
调用thenRun方法执行第二个任务时,则第二个任务和第一个任务时共用同一个线程池
调用thenRunAsync执行第二个任务时,则第一个任务使用的是你自定义的线程池,第二个任务使用的是ForkJoin线程池
备注:可能是线程处理太快,系统优化切换原则,直接使用main线程处理,thenAccept和thenAcceptAsync,thenApply和thenApplyAsync等,之间的区别同理。
4.4 对计算速度进行选用
Java @Slf4j ( topic = "c.CompletableFutureApiDemo" )
public class CompletableFutureApiDemo {
public static void main ( String [] args ) {
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors . newFixedThreadPool ( 3 );
CompletableFuture < String > playA = CompletableFuture . supplyAsync (() -> {
try {
log . debug ( "A come in" );
TimeUnit . SECONDS . sleep ( 2 );
log . debug ( "A complete" );
} catch ( InterruptedException e ) {
e . printStackTrace ();
}
return "playerA" ;
}, threadPool );
CompletableFuture < String > playB = CompletableFuture . supplyAsync (() -> {
try {
log . debug ( "B come in" );
TimeUnit . SECONDS . sleep ( 3 );
log . debug ( "B complete" );
} catch ( InterruptedException e ) {
e . printStackTrace ();
}
return "playerB" ;
}, threadPool );
CompletableFuture < String > result = playA . applyToEither ( playB , f -> f + " is winner" );
log . debug ( "result: {}" , result . join ());
threadPool . shutdown ();
/*
13:36:40.505 c.CompletableFutureApiDemo [pool-1-thread-1] - A come in
13:36:40.505 c.CompletableFutureApiDemo [pool-1-thread-2] - B come in
13:36:42.511 c.CompletableFutureApiDemo [pool-1-thread-1] - A complete
13:36:42.512 c.CompletableFutureApiDemo [main] - result: playerA is winner
13:36:43.507 c.CompletableFutureApiDemo [pool-1-thread-2] - B complete
*/
}
}
4.5 对计算结果进行合并
两个CompletableStage任务都完成后,最终能把两个任务的结果一起交给thenCombine来处理
先完成的先等着,等待其他分支任务
Java @Slf4j ( topic = "c.CompletableFutureApi3Demo" )
public class CompletableFutureApi3Demo {
public static void main ( String [] args ) {
CompletableFuture < Integer > completableFuture1 = CompletableFuture . supplyAsync (() -> {
log . debug ( "启动" );
try {
TimeUnit . SECONDS . sleep ( 1 );
} catch ( InterruptedException e ) {
e . printStackTrace ();
}
return 10 ;
});
CompletableFuture < Integer > completableFuture2 = CompletableFuture . supplyAsync (() -> {
log . debug ( "启动" );
try {
TimeUnit . SECONDS . sleep ( 2 );
} catch ( InterruptedException e ) {
e . printStackTrace ();
}
return 20 ;
});
CompletableFuture < Integer > finalResult = completableFuture1 . thenCombine ( completableFuture2 , ( x , y ) -> {
log . debug ( "开始合并结果" );
return x + y ;
});
log . debug ( "{}" , finalResult . join ());
/*
13:40:48.019 c.CompletableFutureApi3Demo [ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-1] - 启动
13:40:48.019 c.CompletableFutureApi3Demo [ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-2] - 启动
13:40:50.024 c.CompletableFutureApi3Demo [ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-2] - 开始合并结果
13:40:50.025 c.CompletableFutureApi3Demo [main] - 30
*/
}
}
2025-03-16
GitHub